“Tanyuan Initiative” 2024: Recreating the Splendid Grace of the Thousand-year-old Han Dynasty Brocades in Mawangdui through Digital Simulation Restoration Technology
On May 16, the Hunan Museum held the themed promotional event “Hunan Charm: A New Birth”, and grandly unveiled the phased collaborative achievements of the “Tanyuan Initiative 2024”—an intelligent digital simulation restoration project for silk cultural relics from Mawangdui, Hunan. The project aims to reconstruct historical contexts through digital technology, break down temporal and spatial barriers with innovative experiences, assist in solving the common challenge of digital restoration of ancient fragile silk cultural relics within the industry, and usher in a new chapter of “integration of traditional culture and technology”.
The “Tanyuan Initiative 2024” is guided by the Department of Science and Technology Education of the National Cultural Heritage Administration, and initiated by the China Cultural Heritage Information and Consulting Center (Data Center of the National Cultural Heritage Administration), Tencent SSV Digital Culture Lab, Tencent Research Institute, and China Alliance of Social Value Investment (Shenzhen). Aiming to address key common challenges in the industry, the scene co-creation project of “Tanyuan Initiative 2024” selects specific scenarios for innovative exploration and practice of digital technologies and realizes innovative exploration and on-the-ground verification of innovative technology applications in specific cultural contexts, promoting the transformation of co-created achievements.
The Hunan Museum has proposed that innovative technologies are urgently needed to address the core challenge in scenarios where ancient silk clothing cultural relics are fragile and vulnerable, unable to be fully unfolded or completely collected in their original form through wearing. Due to the high importance, urgency, and universality of this scenario requirement within the industry, and its close alignment with the theme, core objectives, and funding direction of the “Tanyuan Initiative 2024”, the Hunan Museum’s scenario was successfully selected for the cultural scene projects of the “Tanyuan Initiative 2024”.
With the innovative funding and support of the “Tanyuan Initiative 2024”, the Hunan Museum has collaborated with Beijing Zhixin Technology Co., Ltd. to carry out innovative exploration and practice in specific scenarios. Through AI technological innovation, the project has achieved intelligent digital simulation restoration of silk cultural relics unearthed from the Mawangdui Han Tombs. This project not only salvages and preserves these precious textiles that bear the code of Chinese civilization, but also completely retains the genetic legacy of traditional craftsmanship on the verge of extinction, opening up a new path for the inheritance and protection of ancient costume culture.


The Exploring the Origin Project supports the challenges of restoring the ultimate craftsmanship of cultural relics
The “Tanyuan Initiative 2024” Intelligent Digital Simulation Restoration Project for Silk Cultural Relics from Mawangdui, Hunan (hereinafter referred to as “this project”) takes AI digital technology as its core and conducts in-depth exploration of the processes and methods for digital simulation restoration of fragile silk cultural relics. The restoration object of this project is the Early Western Han Dynasty noblewoman’s treasure costume unearthed from the Mawangdui Han Tombs—The Ochre Yellow Gauze Ground Stencil-printed and Pigment-painted Silk Robe with Silk Floss Interlining. Its three-layer composite structure (stencil-printed and pigment-painted gauze, silk floss and silk) , complex patterns, and “painted clothing” craftsmanship undoubtedly pose enormous challenges for the digital restoration of silk cultural relics. Under the innovative funding and co-creation incubation mechanism of Tencent’s Exploring the Origin Project, Tencent provided support in startup capital, technology, experts, and innovative models, and the technical party, Beijing Zhixin Technology Co., Ltd., successfully developed a set of digital restoration technical approaches. By adopting technical means of physical imitation combined with a series of AI-assisted tools, it achieved high-precision modeling of the cultural relic itself and all-round restoration of dynamic effects.
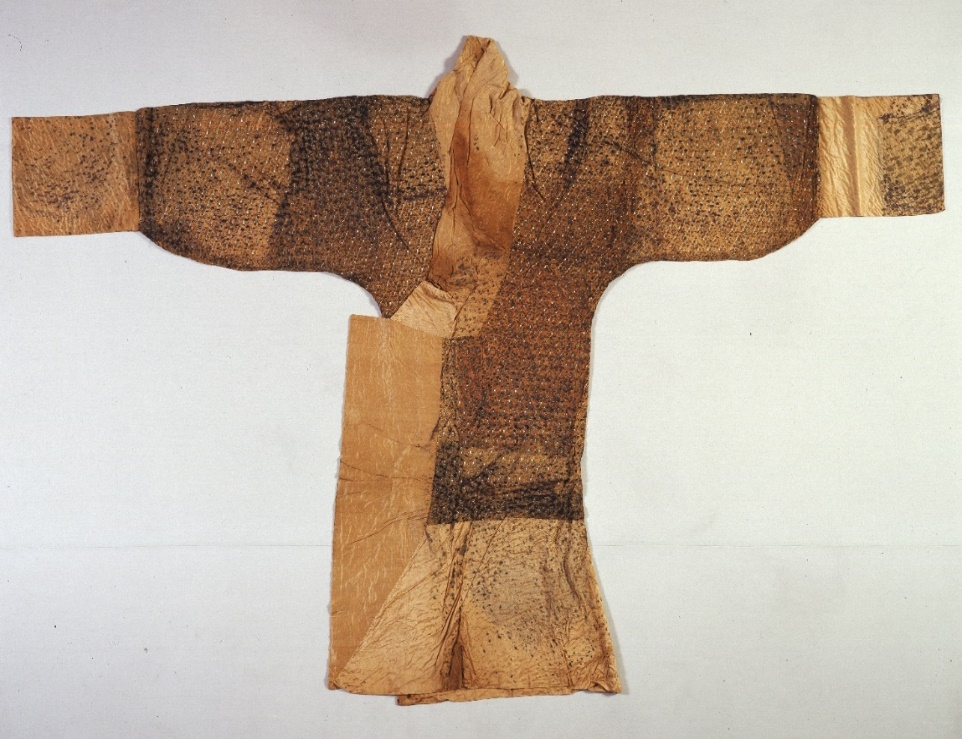

The Ochre Yellow Gauze Ground Stencil-printed and Pigment-painted Silk Robe with Silk Floss Interlining
Four major “first-time” innovations by the Hunan Museum have achieved quality improvement and efficiency enhancement in cultural relic restoration
Through breakthroughs in AI innovative technologies, this project has achieved four major “first-time” innovations:
1.The Hunan Museum’s first-time millimeter-level recreation of the ultimate craftsmanship of silk cultural relics from the Mawangdui Han Tombs
To truly recreate the “painted clothing” craftsmanship, AI was used for auxiliary pattern generation. By training with multimodal cultural relic data (such as vector pattern diagrams and high-definition images), intelligent patterns matching the cultural relics’ style and decorative features were generated based on diffusion models and Controlnet. It supports parameterized adjustments (such as pattern density and symmetry), ultimately outputting high-fidelity digital layers to achieve “thousands of unique patterns”. The time required to generate precise patterns is only 1/3 of that for hand-drawing.
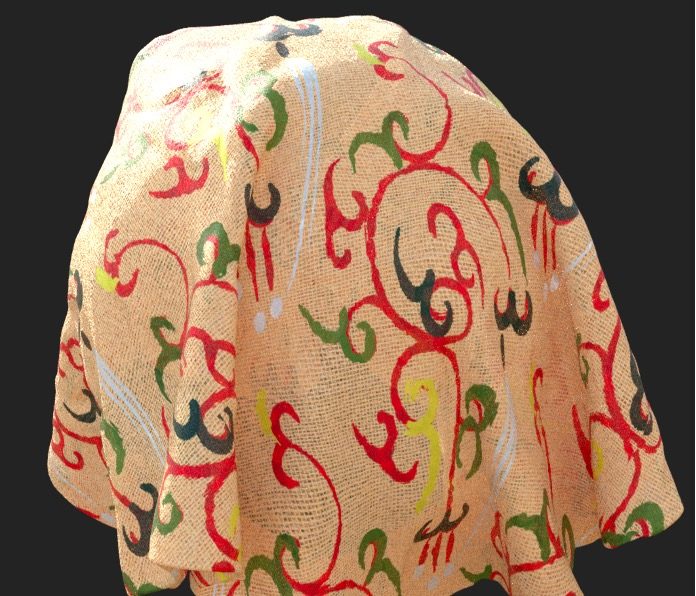

“Microscope-level” ultra-high-definition digital simulation of texture patterns
2.The Hunan Museum has achieved two restoration concepts—“restoring to as-new condition” and “restoring to original appearance”—simultaneously for the silk cultural relics from the Mawangdui Han Tombs for the first time
To genuinely implement the concept of “restoring to original appearance”, AI was used to assist in extracting soiling features. A multi-scale convolutional neural network and a vision Transformer architecture were adopted to automatically extract image features such as stains and dye diffusion on the cultural relic clothing. Cross-domain feature alignment was carried out through pre-trained models, and the representation of key areas (such as edges) was strengthened by combining the attention mechanism. A soiling feature layer was constructed to achieve “digital aging”. This has increased the efficiency by a hundredfold compared with manual extraction.

3D Digital Simulation Models of “Old Clothes” and “New Clothes”
3. The Hunan Museum has for the first time integrated multiple cross-disciplinary technologies with research achievements on silk cultural relics from the Mawangdui Han Tombs
AI industrial quality inspection technologies were applied to “restoration accuracy inspection” for cultural relic simulation: Using a hybrid deep learning and vision Transformer model, algorithm models such as object detection, semantic segmentation, and defect classification were employed to automatically identify the feature matching degree between simulated patterns and original artifacts. Positions with low matching accuracy were automatically annotated to achieve “restoration accuracy inspection”. This has increased efficiency by 20 times compared to manual quality inspection.
AI industrial quality inspection technology is applied to the “restoration accuracy inspection” of cultural relic simulation
4. The Hunan Museum has for the first time truly reproduced the draping texture and dynamic effects of Western Han Dynasty silk costumes
To authentically restore the dynamic texture of cultural relics, we innovatively applied physical imitation and physical motion capture technology to the simulation and restoration of cultural relics. Based on physical motion capture technology, three-dimensional spatial movement data of imitated clothing was collected in real time using optical/inertial sensors and depth cameras. Motion capture algorithms were used to extract features from movement trajectories, while parameter adjustments were made synchronously to truly reproduce the draping texture and dynamic effects of silk cultural relics.
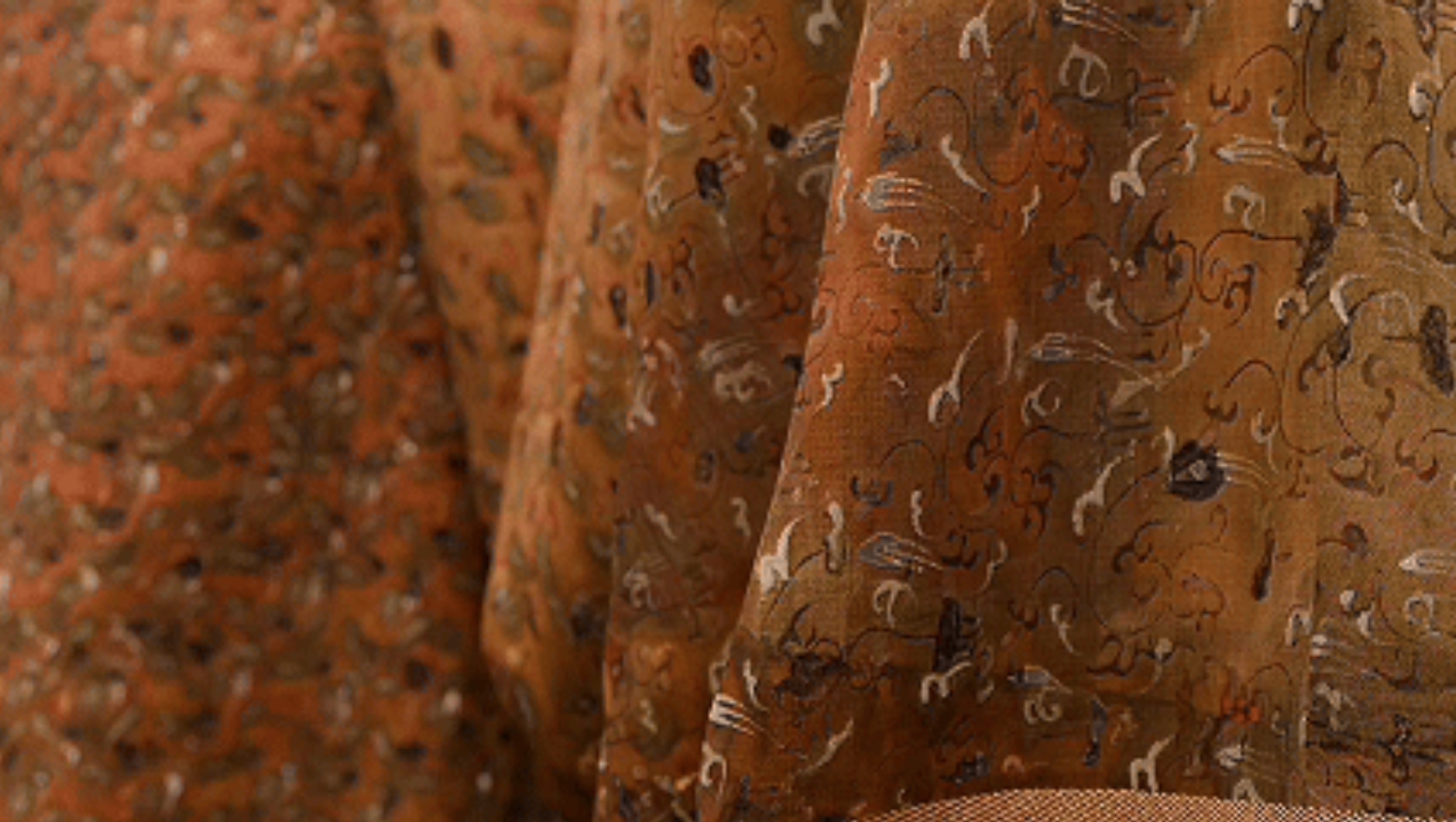

Motion capture technology restores the draping texture and dynamic effects of silk cultural relics
Building up three core data assets to achieve technological inclusivity
This project actively explores an innovative paradigm where technology empowers Chinese culture to glow with vitality, showcasing the detailed aesthetics, craftsmanship, historical charm, and dynamic beauty of silk clothing cultural relics from the Mawangdui Han Tombs, and granting these ancient silk cultural relics a “digital rebirth”. Meanwhile, this project will build up three core digital assets on Tencent SSV’s Exploring the Origin Platform, including:
A comprehensive and refined dataset of the Ochre Yellow Gauze Ground Stencil-printed and Pigment-painted Silk Robe with Silk Floss Interlining from the Mawangdui Han Tombs in Hunan
A 3D simulated clothing model of the Ochre Yellow Gauze Ground Stencil-printed and Pigment-painted Silk Robe with Silk Floss Interlining from the Mawangdui Han Tombs in Hunan, with vivid details and extremely high restoration accuracy;
Clothing display scenarios that present the dynamic effects of ancient clothing in specific contexts
Through building up data assets, technologies, and processes, this project plans to launch reusable digital tools in the future, forming more mature industrial solutions for the restoration and vibrant presentation of similar cultural relics such as silk fabrics and ancient costumes. This project’s collaborative co-creation model helps rapidly replicate technologies to similar cultural relics or different relic domains in the industry, providing a new paradigm of “technological inclusivity” for cultural relics museums and protection institutions.
The spirit of AI silk artisans achieves digital eternity for cultural relics
What touches people deeply about this project is the team of “AI silk artisans”. They are driven by reverence for cultural relics and a sense of mission to inherit civilization, and every line of their code freezes the relics’ twin state in the digital spacetime. Through 1,000 hours of refinement and correction, sub-pixel-level precision at 800K resolution (an unprecedented peak in restoration accuracy), 10TB of process data, and top-tier AI hardware support with 8-GPU film-grade post-production capabilities, the team has used advanced equipment to spare no effort in acquiring comprehensive and accurate data. Meanwhile, cross-disciplinary and cross-domain collaboration provides scientific references for AI reasoning and exploration, while continuous self-iteration and optimization enable the model to infinitely approach the relics in the digital world.
The project leader stated, “This is not just the restoration of a single cultural relic. It marks the first collaboration between traditional silk artisans and young AI digital artisans, and more importantly, a digital decoding of the Western Han Dynasty’s clothing system and dyeing techniques.”
Currently, the project has completed a 3D simulated clothing model of the Ochre Yellow Gauze Ground Stencil-printed and Pigment-painted Silk Robe with Silk Floss Interlining from the Mawangdui Han Tombs in Hunan, and created digital scene display content for the ultimate craftsmanship of the clothing restoration. The follow-up results are expected to be exhibited at the Hunan Museum by the end of June.



